Choose Renvela for its superior phosphate-binding capability and convenient administration. With a more effective formulation, Renvela acts quickly to help manage serum phosphate levels in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). This powder formulation dissolves easily in beverages, making it easier for individuals to incorporate into their daily routine.
Renagel offers a solid alternative, but its tablet form may pose challenges for those who struggle with swallowing pills. Although it is effective in phosphate management, users may find the powder form of Renvela more user-friendly. Both medications serve a similar purpose, but the choice largely depends on personal preference and specific health needs.
Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best option for your treatment plan. Understanding the differences between these two medications will empower you to make an informed decision that aligns with your lifestyle and medical requirements.
- Renvela vs Renagel: A Detailed Comparison
- Mechanism of Action: How Renvela and Renagel Work
- Renvela
- Renagel
- Indications and Uses: When to Choose Renvela or Renagel
- Dosing and Administration: Best Practices for Both Medications
- Renvela Dosing Guidelines
- Renagel Dosing Guidelines
- Side Effects and Contraindications: Understanding the Risks
- Common Side Effects
- Contraindications
Renvela vs Renagel: A Detailed Comparison
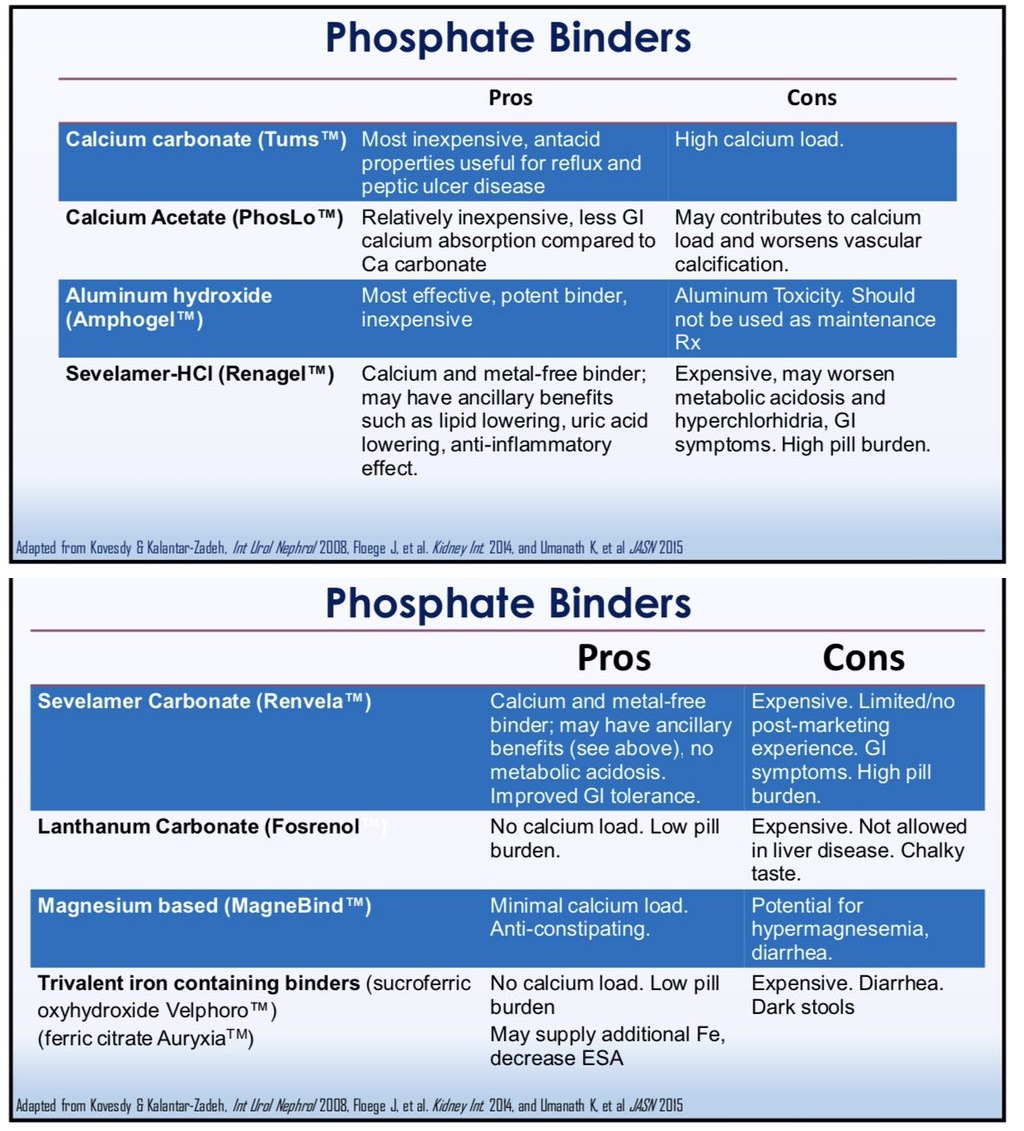
Renvela is a sodium-free phosphate binder primarily used in patients with chronic kidney disease. It effectively reduces serum phosphorus levels in patients on dialysis. Renagel, on the other hand, also functions as a phosphate binder but contains sevelamer hydrochloride and is slightly different in its formulation and application.
Both medications play crucial roles in controlling phosphate levels, but Renvela’s sodium-free formulation can be advantageous for patients who need to manage sodium intake, especially those with hypertension or heart conditions. Renagel may pose a risk of increasing sodium levels, which could complicate treatment for some individuals.
Dosing is another key aspect to consider. Renvela typically has a simpler dosing regimen, allowing for more flexibility in treatment. Patients often find it easier to adhere to Renvela, which can enhance overall compliance with the therapy. Renagel, while effective, may require more frequent monitoring and adjustments in dosage.
Gastrointestinal side effects are noteworthy when comparing these two medications. Both can cause discomfort, but patients on Renvela generally report fewer issues related to gastrointestinal tolerance. This can lead to better quality of life for those undergoing treatment.
Cost may influence your choice as well. Renvela may be more expensive than Renagel, but some patients find it offers better value through improved outcomes and fewer side effects. Discuss with your healthcare provider to determine the best option based on your specific situation, taking into account factors such as insurance coverage and personal health goals.
In summary, both Renvela and Renagel serve their purpose as phosphate binders, but Renvela may offer advantages in terms of sodium content, dosing ease, and gastrointestinal tolerance. An individualized approach will ensure the best results in managing phosphate levels for patients with kidney disease.
Mechanism of Action: How Renvela and Renagel Work
Renvela and Renagel effectively reduce phosphate levels in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) by employing different forms of sevelamer. Their actions involve phosphate binding in the gastrointestinal tract, limiting phosphate absorption.
Renvela
Renvela contains sevelamer carbonate. This formulation offers the advantage of being alkaline, which helps to buffer gastric acid. Renvela binds dietary phosphate by forming insoluble complexes. This process initiates in the stomach and continues in the intestines, where the majority of phosphate absorption occurs.
- Renvela reduces the serum phosphate concentration, leading to improved mineral metabolism.
- Enhancement of gastrointestinal pH can also positively influence calcium and vitamin D metabolism.
Renagel
Renagel consists of sevelamer hydrochloride. Similar to Renvela, it effectively binds phosphate, but its acidic nature can contribute to gastrointestinal side effects. This formulation primarily focuses on preventing phosphate from entering the bloodstream.
- Renagel achieves phosphate control through a similar binding mechanism but may require monitoring due to the potential acid-induced effects on the stomach.
- It is crucial to adhere to prescribed dosages to maintain optimal phosphate management.
Both Renvela and Renagel help patients with CKD manage elevated phosphate levels, but the choice between them can depend on individual tolerance and specific clinical considerations. Regular monitoring of phosphate levels is essential for optimal outcomes.
Indications and Uses: When to Choose Renvela or Renagel
Choose Renvela for patients with chronic kidney disease who require phosphate control and experience gastrointestinal side effects from other phosphate binders. Renvela effectively reduces serum phosphate levels while providing a favorable gastrointestinal profile. Its formulation allows for increased absorption of essential nutrients.
Opt for Renagel if the patient is looking for a non-aluminum, non-calcium phosphate binder and is well-tolerated. Renagel is particularly beneficial for patients who may have concerns regarding calcium intake or those who require strict calcium management. It tends to produce less gastrointestinal discomfort compared to alternatives.
Consider patient preferences and potential drug interactions when deciding between these two options. Both medications serve the same primary purpose but have different formulations that might be better suited to certain medical conditions or lifestyle considerations. Monitor the patient’s response to therapy and adjust as needed. Regular follow-ups to assess serum phosphate levels are crucial in determining the effectiveness of the chosen binder.
Dosing and Administration: Best Practices for Both Medications
Administer Renvela and Renagel according to your healthcare provider’s directions. Both medications contain sevelamer and are used to control phosphorus levels in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis. Adjusting the dose may depend on serum phosphorus levels and dietary intake.
Renvela Dosing Guidelines
For adults, the typical starting dose of Renvela is 800 mg to 1600 mg taken three times a day with meals. Monitor phosphorus levels frequently to determine the proper dosage adjustments. Gradually increase the dose in 800 mg increments until the desired phosphorus level is achieved. Do not exceed 4,800 mg per day.
Renagel Dosing Guidelines
Renagel dosing begins with a recommended starting dose of 800 mg to 1,600 mg taken three times daily with meals. Similar to Renvela, monitor serum phosphorus and adjust the dose as needed. Maintain a maximum daily dose of 6,000 mg. Every patient’s response can differ; therefore, individualization is key.
Both medications should not be crushed or chewed. Take them whole with plenty of water. Effective phosphorus management can lead to improved overall health outcomes in patients undergoing dialysis.
Side Effects and Contraindications: Understanding the Risks
Renvela and Renagel, both phosphate binders, have distinct profiles regarding side effects and contraindications that patients should consider. Awareness of these aspects is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
Common Side Effects
Patients using Renvela may experience gastrointestinal disturbances, including nausea, diarrhea, and constipation. These effects could fluctuate based on dosage adjustments. Renagel, on the other hand, has similar gastrointestinal symptoms, but reports suggest that it may also lead to abdominal discomfort and electrolyte imbalances. Regular monitoring of patients’ digestive health is advisable to manage these reactions swiftly.
Contraindications
Renvela should be avoided in patients with known hypersensitivity to sevelamer or any of its components. For Renagel, contraindications include patients with bowel obstruction, as the formulation may exacerbate this condition. Furthermore, individuals with a history of severe gastrointestinal disorders should discuss their options thoroughly with a healthcare provider. Conducting routine evaluations helps identify any potential contraindications early on.
Informed discussions with healthcare professionals can enhance treatment safety and efficacy, emphasizing the importance of a tailored approach.