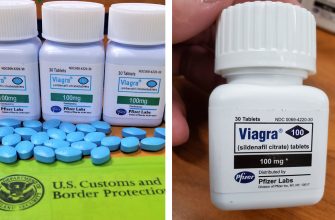
Sildenafil citrate is a prescription medication that effectively treats erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. If you experience difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection, consulting a healthcare provider about this medication might be beneficial. Sildenafil works by increasing blood flow to the penis, which helps to achieve a firm and lasting erection when sexually stimulated.
Typically taken about 30 to 60 minutes before sexual activity, sildenafil’s effects can last up to four hours. It’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s dosage recommendations to maximize results while minimizing the risk of side effects. Starting with a lower dose, such as 25 mg, can be an effective way to gauge tolerance before moving to higher doses, if necessary.
In addition to treating ED, sildenafil is also prescribed for pulmonary arterial hypertension under the brand name Revatio. This can help improve exercise capacity and decrease symptoms in patients with this condition. Understanding the appropriate use and potential interactions with other medications or underlying health issues is critical to ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider will enhance your overall treatment experience. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation, ensuring that sildenafil citrate is both a safe and effective option for you.
- Prescription Sildenafil Citrate
- Understanding the Mechanism of Action of Sildenafil Citrate
- Indications and Dosage Guidelines for Sildenafil Citrate
- Dosage for Erectile Dysfunction
- Dosage for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions with Sildenafil Citrate
- Drug Interactions
- Recommendations
- Patient Considerations and Counseling Points for Sildenafil Citrate
Prescription Sildenafil Citrate
Sildenafil citrate is prescribed primarily for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. The active ingredient enhances blood flow to the penis during sexual stimulation, helping to achieve and maintain an erection. A healthcare provider will typically recommend a starting dose of 50 mg, taken approximately one hour before sexual activity. Adjustments may be made based on individual response and tolerability, with a maximum recommended dose of 100 mg.
Before starting sildenafil, a medical evaluation is essential. Disclose any existing health conditions, particularly heart issues, or medications currently in use. This information helps avoid potential drug interactions and ensures safety during use. Avoid consuming nitrates or other medications that may lower blood pressure, as this can lead to serious complications.
Side effects may include headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. Most side effects typically resolve without further intervention. If you experience severe reactions such as sudden vision loss or an erection lasting more than four hours, seek medical attention immediately.
Combining sildenafil with alcohol can diminish its effectiveness. It’s advisable to limit alcohol intake before use. Engaging in sexual activity should also be approached with caution, particularly for those with underlying health conditions.
Consult your healthcare provider regularly to assess the effectiveness of sildenafil and make necessary adjustments. A successful management plan ensures optimal results aligned with your individual health needs.
Understanding the Mechanism of Action of Sildenafil Citrate
Sildenafil citrate operates primarily as a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor. By blocking the PDE5 enzyme, it prevents the breakdown of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). This process increases the levels of cGMP within the smooth muscle of the penis, leading to the relaxation of blood vessels and enhanced blood flow during sexual stimulation.
Sildenafil citrate is primarily indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). It enhances blood flow to the penis during sexual stimulation, facilitating an erection. Additionally, it is prescribed for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), where it acts as a vasodilator, improving exercise ability and reducing the progression of the disease.
Dosage for Erectile Dysfunction
The recommended starting dose for sildenafil citrate in treating ED is 50 mg, taken approximately one hour before anticipated sexual activity. Depending on effectiveness and tolerance, the dosage can be adjusted to 100 mg or decreased to 25 mg. It is essential to note that the maximum recommended frequency is once per day.
Dosage for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
For the management of PAH, the usual starting dose is 5 mg three times a day. After a few weeks, this may be adjusted to 20 mg three times daily based on tolerability and response. Administering sildenafil with a high-fat meal may delay its absorption, so taking it on an empty stomach is advisable for optimal outcomes.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to your dosage or treatment plan. Regular monitoring ensures the safety and effectiveness of sildenafil citrate in managing both ED and PAH.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions with Sildenafil Citrate
Sildenafil citrate, widely used for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, may lead to various side effects. Commonly reported effects include headaches, flushing, upset stomach, nasal congestion, and dizziness. Less frequently, users might experience changes in vision, such as blurriness or a blue tint to their vision. Severe reactions can occur, including priapism, a painful prolonged erection requiring immediate medical attention, or sudden hearing loss, which also necessitates urgent care.
Drug Interactions
Consider potential interactions with other medications when using sildenafil. Avoid combining it with nitrates, commonly prescribed for chest pain, as this combination can lead to a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Some alpha-blockers can also interact, causing variations in blood pressure. Always disclose all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to your healthcare provider to ensure safety.
Recommendations
Monitor your body’s reactions after taking sildenafil. If side effects persist or worsen, consult your doctor promptly. Regular check-ups can help assess overall health and medication efficacy. Staying informed about potential interactions with other drugs further enhances safety while using sildenafil citrate.
Patient Considerations and Counseling Points for Sildenafil Citrate
Discussing sildenafil citrate with patients involves several key points for effective management and understanding.
- Administration Timing: Advise patients to take sildenafil approximately 30 minutes to 1 hour before anticipated sexual activity. Effects can last up to 4 hours, so timing is essential for optimal results.
- Dosage Information: Start with the recommended dose of 50 mg. Adjustments can be made based on efficacy and tolerability, with a maximum daily dose of 100 mg.
- Food Interaction: Instruct patients that a high-fat meal may delay the onset of action. For best results, take the medication on an empty stomach.
- Alcohol Consumption: Advise limiting alcohol intake, as excessive drinking can impair erectile function and increase the likelihood of side effects.
- Potential Side Effects: Inform patients of common side effects, including headaches, flushing, and indigestion. Severe reactions like sudden vision or hearing loss require immediate medical attention.
- Drug Interactions: Review concurrent medications, particularly nitrates and alpha-blockers, as these can lead to significant interactions and hypotension.
- Medical History: Collect information on cardiovascular issues, as sildenafil can affect blood pressure. Patients with a history of heart problems should consult a healthcare provider before use.
- Psychological Factors: Encourage discussions about psychological or emotional factors that may influence sexual performance. Address any underlying concerns that may benefit from therapy.
- Use with Caution: Advise patients to use sildenafil only under professional guidance, particularly if they have complex health issues or take multiple medications.
Ongoing communication is key. Schedule follow-up appointments to assess effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.