Consider starting with 25mg of Seroquel XR at bedtime. This lower dose often effectively manages symptoms for many individuals, minimizing potential side effects. Remember, individual responses vary greatly.
Your doctor should carefully monitor your progress, adjusting the dosage based on your specific needs and response. Regular blood tests can help track any potential side effects and ensure the medication’s efficacy. Don’t hesitate to communicate openly with your healthcare provider about any concerns or changes you experience.
Important Note: This information serves as a general guideline and does not replace personalized medical advice. Always consult your physician or psychiatrist before starting, stopping, or altering any medication, including Seroquel. They will consider your medical history, current conditions, and other medications to create a safe and effective treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects: Common low-dose side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and weight gain. While these can be manageable, open communication with your doctor is vital. They can help you explore strategies to mitigate these effects or adjust your treatment accordingly.
Low Dose Seroquel: Uses and Indications
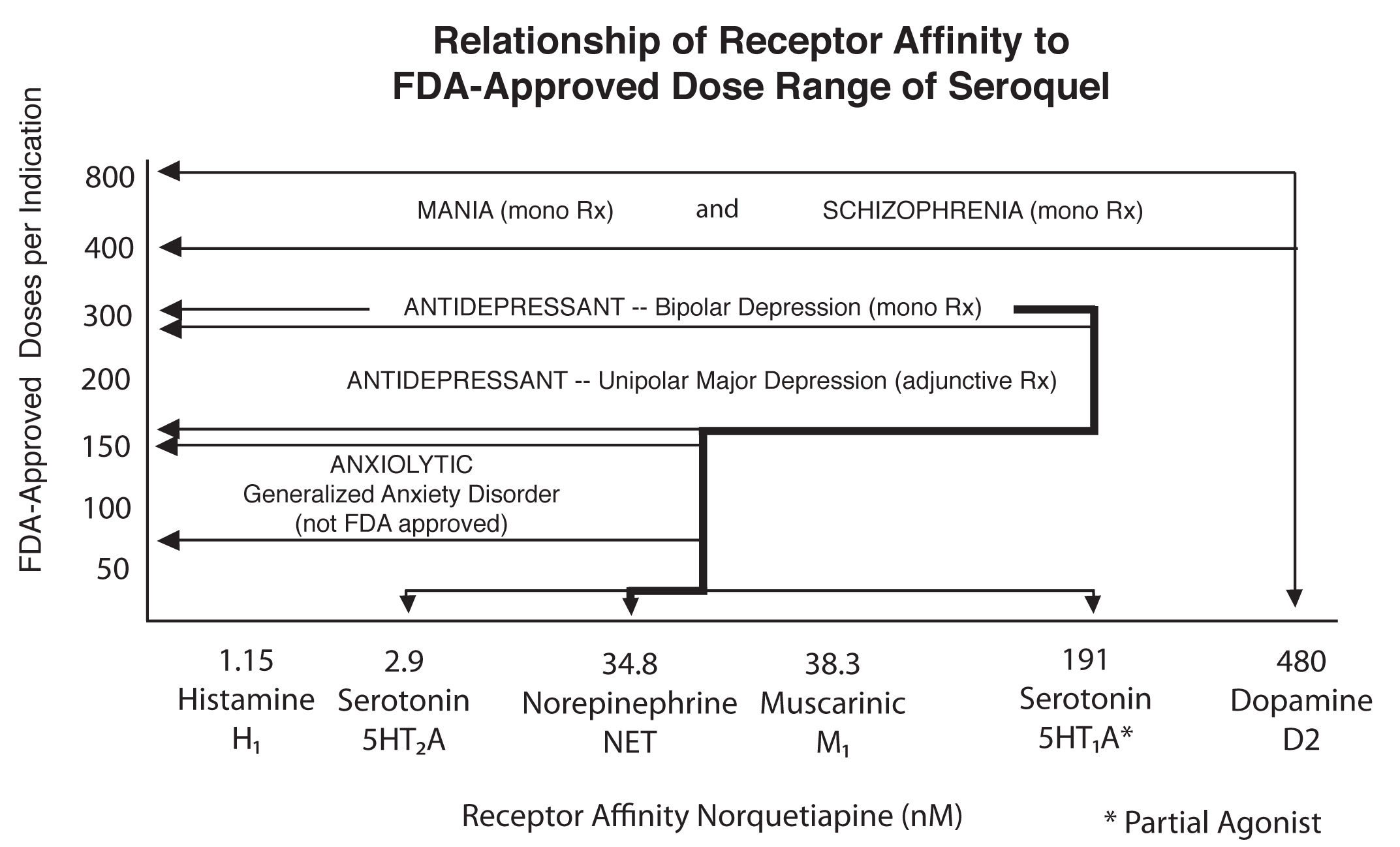
Low-dose quetiapine (Seroquel) finds application primarily in managing insomnia and anxiety. It’s often prescribed off-label for these conditions, meaning its use isn’t formally approved by regulatory bodies for these specific purposes, but it’s a common practice supported by clinical observations.
Specifically, low doses can alleviate symptoms of insomnia by promoting sleep onset and improving sleep quality. This is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, but who don’t require a strong sedative effect. The anxiolytic effects can help manage generalized anxiety disorder symptoms, reducing feelings of nervousness and worry.
Another area where low-dose Seroquel shows promise is as an adjunct treatment for depression. Combined with antidepressants, it might augment their effectiveness, potentially improving mood and reducing depressive symptoms. However, this is also off-label and requires careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
It’s crucial to understand that low-dose Seroquel isn’t a first-line treatment for any of these conditions. Its use should be carefully considered and discussed with a physician. They will assess your individual needs and determine if low-dose Seroquel is appropriate and safe for you.
Prescribing information and dosage will vary based on individual patient factors such as age, other health conditions, and concurrent medications. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and administration.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting or changing any medication.
Low Dose Seroquel: Potential Benefits and Side Effects
Low-dose Seroquel (quetiapine) is sometimes prescribed for conditions beyond its FDA-approved uses. Remember to discuss all treatment options with your doctor.
Potential Benefits:
- Improved sleep: Many users report better sleep quality at lower doses, addressing insomnia without the significant sedation of higher doses.
- Anxiety reduction: Some find low-dose Seroquel helps manage anxiety symptoms, offering a calmer feeling without excessive drowsiness.
- Mood stabilization (in some cases): It might aid in mood stabilization for certain individuals, particularly those with bipolar disorder experiencing mild mood swings.
Side Effects: Even at low doses, side effects can occur. They vary greatly depending on individual factors.
- Drowsiness: Though often less intense at lower doses, drowsiness is a common side effect.
- Weight gain: Weight gain is a potential long-term side effect, though the risk may be reduced with lower doses and lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring is crucial.
- Dizziness and lightheadedness: These can occur, especially when starting treatment. Standing up slowly can help mitigate this.
- Dry mouth: This is a relatively common side effect that may resolve on its own or with increased hydration.
- Constipation: Maintaining adequate hydration and fiber intake can help reduce constipation.
- Metabolic changes: Increased blood sugar and cholesterol levels are potential long-term risks; regular monitoring is recommended.
Important Considerations:
- Dosage: Your doctor will determine the appropriate low dose based on your individual needs and health history. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor.
- Interactions: Seroquel can interact with other medications. Always inform your doctor of all medications and supplements you are taking.
- Monitoring: Regular checkups are crucial to monitor your progress and manage potential side effects.
- Alternative treatments: Low-dose Seroquel may not be suitable for everyone. Discuss all treatment options with your doctor to find the best approach for your specific situation.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional before starting any new medication or changing your current treatment plan.
Low Dose Seroquel: Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage. Typical low-dose Seroquel (quetiapine) ranges from 25mg to 50mg daily, often administered once daily at bedtime. However, your doctor may adjust this based on your individual needs and response to treatment. Some individuals may benefit from a twice-daily regimen, again, as directed by their physician.
Adjusting Your Dosage
Never change your Seroquel dosage without consulting your doctor. Increases should be gradual, typically in 25mg increments at intervals determined by your doctor. They will monitor your response, adjusting the dosage to find the optimal balance of efficacy and tolerability. This careful titration minimizes potential side effects.
Administration
Seroquel tablets are usually swallowed whole with water. Avoid crushing or chewing the tablets. Take the medication with food to reduce potential stomach upset. Consistent timing is recommended for best results. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to your next scheduled dose. Never double up on doses.
Monitoring and Side Effects
Regular check-ups with your doctor are critical for monitoring your progress and managing potential side effects. Common side effects can include drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, and dry mouth. Report any significant side effects or changes in your condition immediately to your healthcare provider. Open communication with your doctor is key to successful treatment.
Low Dose Seroquel: Risks and Considerations
Consult your doctor before starting or altering your Seroquel dosage. Low doses, while sometimes effective for specific conditions, may still carry risks.
Weight gain is a common side effect, even at low doses. Monitor your weight regularly and discuss strategies for managing weight gain with your healthcare provider. Dietary changes and exercise are often recommended.
Drowsiness is another potential side effect. If you experience excessive sleepiness, adjust your dosage timing or discuss alternative treatment options with your doctor. Avoid driving or operating machinery if you feel drowsy.
Metabolic changes, including increased blood sugar and cholesterol, can occur. Regular blood tests are crucial to monitor these levels. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes or additional medication to manage these risks.
Though less frequent at low doses, dizziness and orthostatic hypotension (a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing) are possible. Rise slowly from sitting or lying positions. Report any significant dizziness to your doctor immediately.
Some individuals experience movement disorders at any dosage. This includes symptoms like tremors or rigidity. Report any unusual movements to your doctor promptly.
Anticholinergic effects are possible at low doses. This might manifest as dry mouth or constipation. Increase fluid intake and fiber to address these issues. However, severe anticholinergic effects warrant immediate medical attention.
Interactions with other medications are possible. Provide a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies to your doctor or pharmacist before starting Seroquel.
Individual responses to Seroquel vary significantly. What works for one person may not work for another. Open communication with your doctor is key to optimizing your treatment and managing potential side effects.