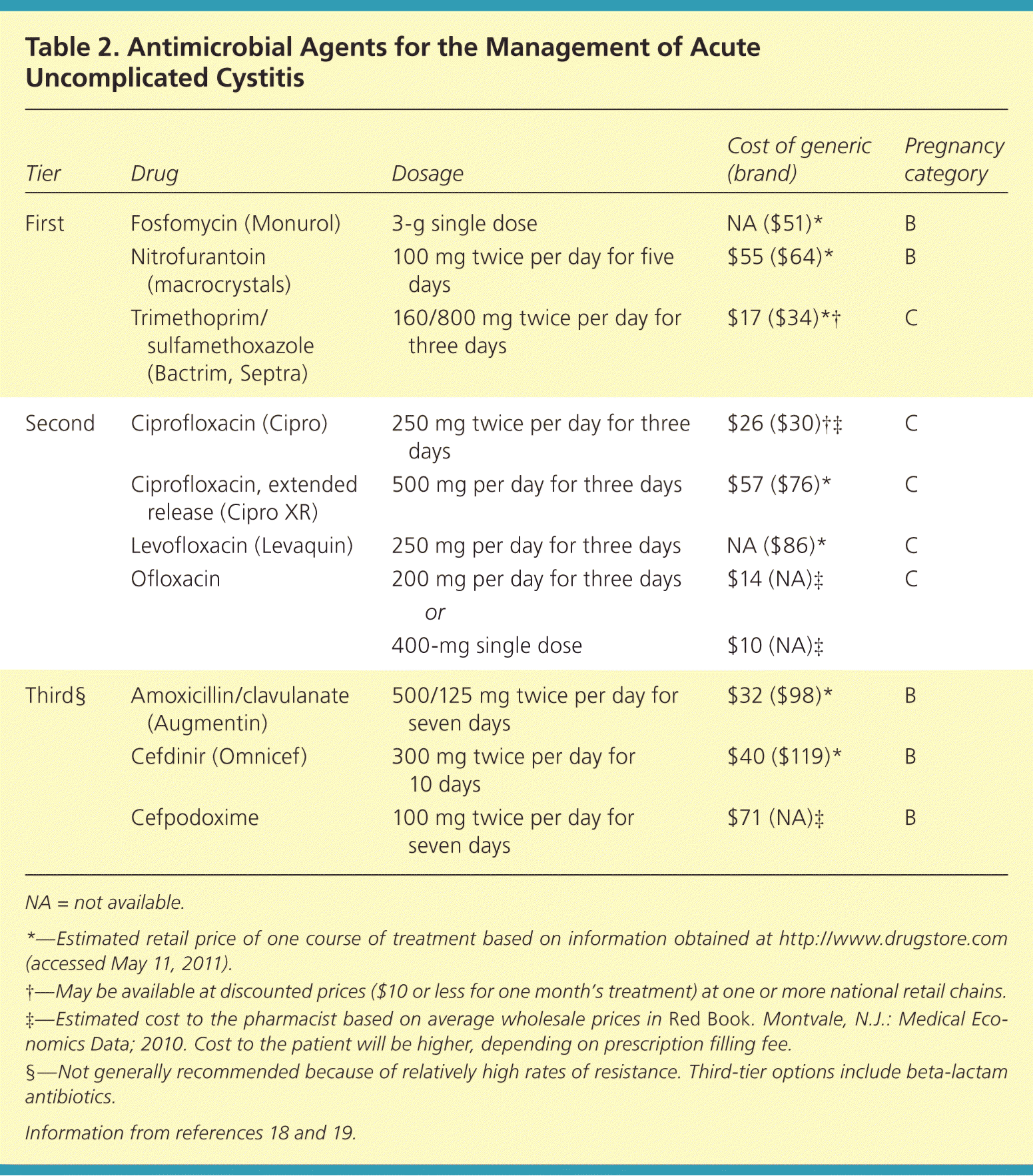
For uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), a common treatment is Ciprofloxacin (Cipro). A typical adult dose is 250 mg twice daily for 3 to 7 days. This dosage may vary based on individual factors, so always follow your doctor’s specific instructions.
Important Note: This is general guidance only. Your doctor will consider your medical history, the severity of your infection, and other factors to determine the appropriate dose and duration of Cipro treatment. Never adjust your medication without consulting a healthcare professional.
Factors influencing dosage: Kidney function plays a crucial role. Individuals with impaired kidney function may require a lower dose or less frequent administration. Similarly, age and other health conditions might affect the recommended dosage. Your doctor will adjust the prescription as needed.
Potential Side Effects: While generally well-tolerated, Cipro can cause side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Rare but serious side effects exist. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Alternatives to Cipro: If you have allergies or other contraindications to Cipro, alternative antibiotics are available. Your physician will choose the most suitable option for your situation.
- Cipro Dose for Uncomplicated UTI
- Standard Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Uncomplicated UTIs
- Understanding Uncomplicated vs. Complicated UTIs
- Uncomplicated UTIs
- Complicated UTIs
- Important Note: Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Self-treating UTIs can lead to serious complications.
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Severe Symptoms Requiring Immediate Care
Cipro Dose for Uncomplicated UTI
For most adults with an uncomplicated UTI, the typical Ciprofloxacin dose is 250 mg twice daily for 3-7 days. Your doctor will determine the precise duration based on your individual symptoms and response to treatment.
A shorter course of 3 days may be sufficient for some, while others might require the full 7-day regimen. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and treatment duration.
Children and individuals with kidney problems usually require adjusted dosages. Your healthcare provider will calculate the appropriate dose based on your age, weight, and kidney function.
Never adjust your Ciprofloxacin dosage without consulting your doctor. Incorrect dosing can lead to treatment failure or adverse effects.
If you experience any side effects, such as nausea, diarrhea, or allergic reactions, contact your doctor immediately. Early reporting is key for managing potential complications.
Remember, this information is for guidance only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician for diagnosis and treatment of UTIs.
Standard Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Uncomplicated UTIs
For most adults with uncomplicated UTIs, the standard Ciprofloxacin dosage is 250 mg twice daily for 3-7 days. Your doctor will determine the precise duration based on your individual needs and response to treatment.
A 500 mg once-daily regimen might be considered, but this should only be done under strict medical supervision and is not the typical approach.
Children and individuals with kidney problems require adjusted dosages; always follow your doctor’s specific instructions. Never adjust your medication without consulting your physician.
This information serves as a general guide. Individualized treatment plans are critical. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment of a UTI.
Understanding Uncomplicated vs. Complicated UTIs
A key distinction in UTI treatment is whether the infection is uncomplicated or complicated. This affects treatment choices, including Ciprofloxacin dosage.
Uncomplicated UTIs
Uncomplicated UTIs generally affect healthy women (ages 18-65) with no structural abnormalities or underlying medical conditions that could hinder their ability to fight off infection. They usually involve only the bladder (cystitis). Treatment often involves a 3-day course of antibiotics.
Complicated UTIs
Complicated UTIs present a different picture. These infections may involve the kidneys (pyelonephritis), occur in men, pregnant women, or individuals with compromised immune systems, urinary tract abnormalities (e.g., kidney stones, vesicoureteral reflux), or indwelling catheters. Treatment is more complex and may involve longer antibiotic courses, different antibiotics (possibly not Cipro), or hospitalization.
| Characteristic | Uncomplicated UTI | Complicated UTI |
|---|---|---|
| Patient Population | Healthy women (18-65), no underlying conditions | Men, pregnant women, immunocompromised individuals, those with urinary tract abnormalities |
| Location of Infection | Usually bladder only (cystitis) | May involve bladder, kidneys (pyelonephritis), or other urinary tract structures |
| Treatment Duration | Often 3 days | Usually longer, may require hospitalization |
| Antibiotic Choice | Often first-line antibiotics like nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | May necessitate different antibiotics or combinations, depending on the specific case |
Important Note: Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Self-treating UTIs can lead to serious complications.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Ciprofloxacin, while effective for uncomplicated UTIs, can cause side effects. These vary in severity and frequency.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These usually are mild and resolve without treatment. However, severe diarrhea might indicate Clostridium difficile infection, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Take Cipro with food to minimize these.
- Diarrhea: Report persistent or severe diarrhea to your doctor. Avoid anti-diarrheal medications unless advised by your physician.
- Abdominal Pain: If pain is severe or persistent, consult your doctor.
Less common but more serious side effects include:
- Tendinitis and Tendon Rupture: This is more likely in older adults and those taking corticosteroids. Report any tendon pain immediately.
- Allergic Reactions: Symptoms range from rash to severe anaphylaxis. Stop taking Cipro and seek immediate medical help if you experience an allergic reaction.
- Central Nervous System Effects: Headache, dizziness, confusion, and seizures are possible, though rare. Report any neurological changes promptly.
- Photosensitivity: Avoid prolonged sun exposure while taking Cipro.
Before starting Cipro, inform your doctor about:
- Existing medical conditions, particularly kidney or liver problems.
- Other medications you are taking, including supplements and herbal remedies.
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Any history of allergic reactions to antibiotics.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking Cipro prematurely, even if you feel better. Completing the prescribed course ensures effective treatment and reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your doctor immediately if your symptoms worsen or don’t improve after three days of taking Cipro. This includes persistent or increasing pain, fever above 101°F (38.3°C), or chills.
Severe Symptoms Requiring Immediate Care
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following: severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting that prevents you from keeping down fluids, blood in your urine, or signs of dehydration such as dizziness or lightheadedness. These may indicate a more serious infection requiring stronger antibiotics or other interventions.
Allergic reactions, such as hives, rash, swelling, or difficulty breathing, are serious and require immediate medical help. Stop taking Cipro and seek emergency care if you experience any allergic reaction.