Amoxicillin serves as a reliable option for treating skin abscesses, mainly caused by bacterial infections. This antibiotic effectively targets the bacteria responsible for these infections, helping to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Ensure you consult a healthcare professional to confirm that amoxicillin is the right choice for your specific situation.
When prescribed amoxicillin for a skin abscess, follow the dosage instructions closely. Typically, the dose may range from 500 mg taken every 8 hours to 875 mg taken every 12 hours, depending on the severity and location of the infection. Taking the medication with or without food is generally acceptable, which adds convenience to your treatment regimen.
Be vigilant about potential side effects, such as nausea, diarrhea, or allergic reactions. If any severe symptoms occur, such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat, seek immediate medical attention. Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for monitoring your progress throughout the treatment.
While amoxicillin can effectively manage many skin abscess cases, it’s essential to combine it with proper wound care and, if necessary, drainage procedures. Discuss your treatment plan with your healthcare provider to ensure optimal recovery.
- Amoxicillin for Skin Abscess
- Understanding Skin Abscesses: Causes and Symptoms
- Mechanism of Action: How Amoxicillin Works Against Infections
- Indications for Amoxicillin in Treating Skin Abscesses
- Clinical Circumstances for Amoxicillin Use
- Adjunctive Therapy Considerations
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration Methods for Amoxicillin
- Administration Methods
- Special Considerations
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Using Amoxicillin
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common Risks
- When to Seek Medical Attention: Signs That Require Urgent Care
Amoxicillin for Skin Abscess
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for skin abscesses caused by certain bacteria. This antibiotic works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, effectively targeting infections and promoting healing.
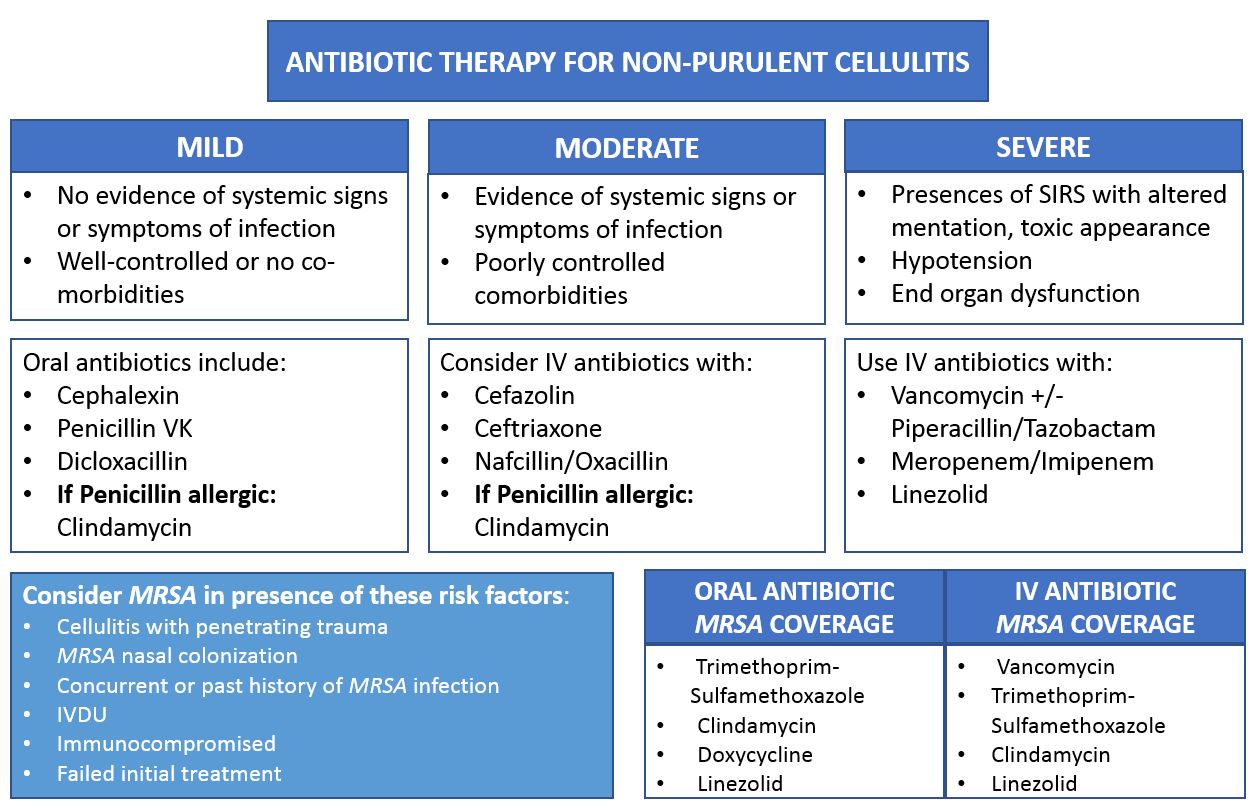
For most cases of skin abscess, a healthcare provider may recommend the following:
- Dosage: Typical dosages for adults range from 250 mg to 500 mg every 8 hours, or 500 mg to 875 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection.
- Duration: Continue the treatment for 5 to 10 days, based on the healthcare provider’s assessment.
- Administration: Take Amoxicillin with or without food. Drinking a full glass of water is encouraged.
Monitoring for side effects is vital. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and rash. If severe allergic reactions or symptoms such as difficulty breathing occur, seek immediate medical attention.
For optimal effectiveness, follow these practices:
- Complete the full course of antibiotics even if symptoms improve.
- Avoid sharing medications with others.
- Inform your healthcare provider about any other medications being taken to prevent interactions.
In some instances, drainage of the abscess may also be necessary. This procedure helps reduce infection and enhances the antibiotic’s effectiveness.
Consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen after starting Amoxicillin. Follow their guidance for any adjustments or additional treatments required for recovery.
Understanding Skin Abscesses: Causes and Symptoms
Skin abscesses form due to localized infection, leading to the accumulation of pus beneath the skin. They usually arise from bacteria entering through cuts, insect bites, or clogged sweat glands. Staphylococcus aureus is a common culprit, but other bacteria can also cause abscesses.
Common symptoms include a painful, swollen area of the skin that feels warm to the touch. The affected area may appear redder than surrounding skin, and you might notice a visible pocket of pus, sometimes with a central point. Fever and chills can occur if the infection spreads, indicating a more serious condition that may require medical attention.
If you suspect a skin abscess, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment. Drainage of the abscess is often necessary, alongside antibiotics like amoxicillin to combat infection. Early intervention helps mitigate complications and enhances recovery.
Mechanism of Action: How Amoxicillin Works Against Infections
Amoxicillin targets bacteria by inhibiting their cell wall synthesis. It binds to specific proteins, known as penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), which play a key role in the formation of the bacterial cell wall. This binding prevents the bacteria from strengthening their cell walls, leading to cell lysis and death.
This antibiotic is effective against a broad spectrum of gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. In skin abscesses, these bacteria often contribute to infection. By disrupting the production of the cell wall, amoxicillin effectively diminishes the bacteria’s ability to survive and multiply.
In some cases, the bacteria may produce beta-lactamase, an enzyme that renders amoxicillin ineffective. To address this, combination therapies using amoxicillin along with clavulanate potassium are utilized. Clavulanate inhibits beta-lactamase, enhancing amoxicillin’s efficacy against resistant strains.
Amoxicillin exhibits a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, allowing for convenient dosing. It achieves optimal concentrations in body tissues, including the skin, thus effectively treating abscesses. Administering amoxicillin as prescribed is crucial for maximizing its antibacterial activity and ensuring complete resolution of the infection.
Indications for Amoxicillin in Treating Skin Abscesses
Amoxicillin is recommended for treating skin abscesses primarily caused by susceptible bacteria, particularly during initial management. This antibiotic is most effective for infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Clinical Circumstances for Amoxicillin Use
Consider using Amoxicillin when patients present with mild to moderate skin abscesses that have not progressed to severe systemic infection or necrotizing fasciitis. It’s suitable for cases where culture results indicate sensitivity to this antibiotic, potentially guiding therapy for uncomplicated abscesses. For individuals with no history of penicillin allergy, Amoxicillin serves as a reliable oral option.
Adjunctive Therapy Considerations
In some situations, Amoxicillin may be combined with other therapies, especially if polymicrobial infection is suspected. Incision and drainage remain critical steps in management, and Amoxicillin aids in covering additional bacterial flora that may be present, including anaerobic bacteria. Always assess the patient’s overall health and local resistance patterns before prescribing.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration Methods for Amoxicillin
For treating skin abscesses, the typical dosage of amoxicillin for adults is 500 mg every eight hours or 875 mg every twelve hours. Adjustments may be necessary based on the severity of the infection and patient response. For pediatric patients, the standard dose ranges from 20 to 40 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses, not exceeding 1,000 mg per day.
Administration Methods
Amoxicillin is available in several forms: capsules, tablets, and oral suspension. Take the capsules or tablets with a full glass of water, ideally one hour before or two hours after meals for optimal absorption. If you prefer the oral suspension, shake the bottle well before measuring the prescribed amount. Use a medicine syringe or cup for accurate dosing.
Special Considerations
Monitor for allergic reactions, especially in patients with a history of penicillin allergies. Adjust dosages for patients with renal impairment, typically recommending a dosage reduction based on the degree of renal dysfunction. For long-term treatments, periodic assessments of liver and renal function are advisable.
Consistency is key; encourage patients to complete the full course of amoxicillin, even if symptoms improve early. This helps prevent the development of resistant bacteria.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Using Amoxicillin
Patients taking amoxicillin should be aware of potential side effects that may arise during treatment. While the medication is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience adverse reactions.
Common Side Effects
Among the most frequent side effects of amoxicillin are gastrointestinal issues. Diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting may occur, potentially leading to dehydration. Maintaining hydration during treatment is crucial. Allergic reactions can also manifest, ranging from mild rash to severe anaphylaxis. Seek medical attention immediately if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling, or hives.
Less Common Risks
Less frequently, patients may experience liver-related issues indicated by jaundice or dark urine. Blood disorders, such as thrombocytopenia, can also arise, affecting blood clotting. Regular blood tests may be necessary for those with pre-existing conditions affecting blood health.
| Side Effect | Symptoms | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal Issues | Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting | Stay hydrated, consult a doctor if severe |
| Allergic Reactions | Rash, swelling, difficulty breathing | Seek emergency medical help |
| Liver Issues | Jaundice, dark urine | Consult a healthcare provider |
| Blood Disorders | Unusual bruising, prolonged bleeding | Get regular blood tests; seek medical care if symptoms appear |
Monitor your health closely while using amoxicillin, and communicate any concerns with your healthcare provider. Prompt reporting of side effects can lead to timely adjustments in your treatment plan.
When to Seek Medical Attention: Signs That Require Urgent Care
If you notice any of the following signs, seek medical attention promptly:
- Increased Redness and Swelling: Rapid expansion of redness or swelling around the abscess may indicate an infection spreading beyond the initial site.
- Fever: A temperature of 101°F (38.3°C) or higher may signal a systemic infection that needs immediate treatment.
- Pus or Discharge: If the abscess begins to drain thick, yellowish or greenish pus, this indicates an active infection that may require antibiotic intervention.
- Severe Pain: Escalating pain that does not improve with over-the-counter medications suggests a need for professional evaluation.
- Chills or Sweats: Experiencing chills or night sweats can indicate your body is fighting an infection, potentially needing medical intervention.
- Rapid Heart Rate: A heart rate that exceeds 100 beats per minute while at rest may indicate a serious condition requiring attention.
- Difficulty Breathing: If you experience shortness of breath or any breathing difficulties in conjunction with an abscess, seek help immediately.
- Abscess Larger than a Quarter: If the size of the abscess surpasses a quarter, it’s wise to consult a healthcare provider for assessment and possible drainage.
- Persistent Symptoms: If symptoms do not improve after a few days of home treatment, it’s time for a professional opinion.
Addressing these warning signs early can prevent complications and lead to more effective treatment. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider if you feel uncertain about your situation.