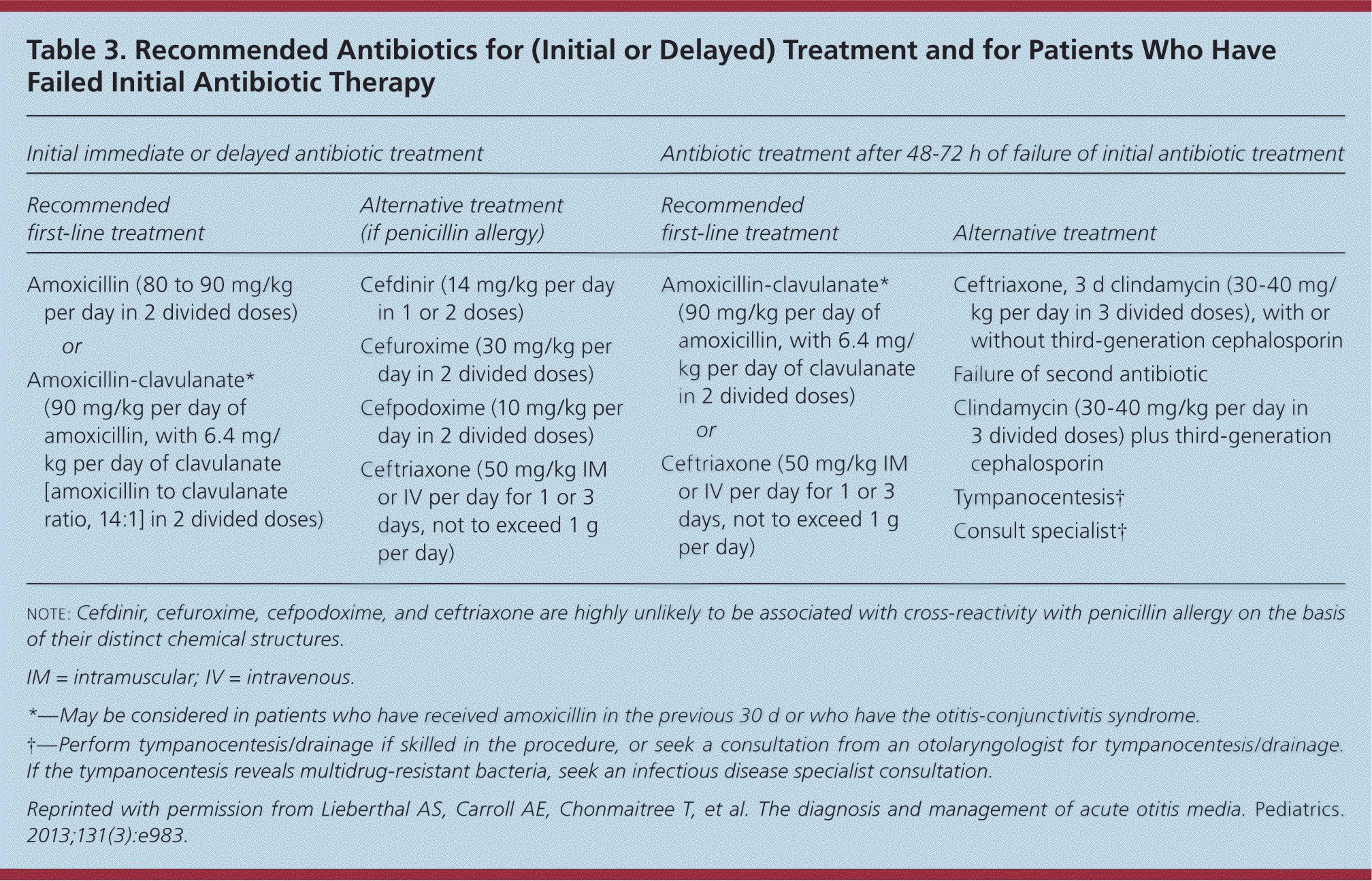
The typical dosage for amoxicillin in treating otitis media in children is 80-90 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. For most pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg, the maximum daily dose should not exceed 1,000 mg. This dosing range ensures effective treatment while minimizing the risk of side effects.
For adults, the standard dose is usually 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours for more severe infections. In cases of antibiotic resistance or recurrent infections, a higher dose of 1,000 mg every 12 hours may be recommended. Close attention to the patient’s response to treatment is crucial to ensure the best outcomes.
Be sure to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any antibiotic therapy. Each patient’s medical history and potential allergies will determine the most appropriate dosage and duration of treatment. Regular follow-ups may be necessary to monitor progress and address any complications that may arise during treatment.
- Amoxicillin Dose for Otitis Media
- Adjustments for Special Cases
- Side Effects and Monitoring
- Understanding Otitis Media and Its Symptoms
- Common Symptoms to Watch For
- Timely Action and Treatment
- Recommended Amoxicillin Dosage for Children
- Recommended Amoxicillin Dosage for Adults
- Factors Influencing Amoxicillin Dosage Adjustments
- Potential Side Effects and Considerations with Amoxicillin
- Allergic Reactions
- Drug Interactions
Amoxicillin Dose for Otitis Media
The recommended dosage of amoxicillin for treating otitis media in children typically ranges from 80 to 90 mg/kg per day, divided into two doses. For mild to moderate infections, 500 mg every 12 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours is common for adults. The treatment duration usually lasts 7 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the infection and the patient’s response to the medication.
Adjustments for Special Cases
For children weighing less than 40 kg, a common approach is to calculate the dose based on weight, ensuring the total does not exceed 1,000 mg per day. Patients with a history of recurrent otitis media may require a higher dose for adequate treatment. Always verify the patient’s medical history and consider any potential allergies or complications that could affect dosing.
Side Effects and Monitoring
Monitor for any side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions. If a patient develops a rash or any severe reaction, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional. Regular follow-ups can help ensure the infection is resolving and that the treatment is effective.
Understanding Otitis Media and Its Symptoms
Otitis media primarily occurs due to infection in the middle ear, often following a cold or other upper respiratory infections. Recognizing its symptoms enables timely intervention. Pay attention to persistent ear pain, irritability in children, fluid drainage from the ear, and difficulty sleeping. These indicators frequently suggest potential ear infections.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Look for the following symptoms that may accompany otitis media:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Ear Pain | Sharp, throbbing pain, especially when lying down. |
| Fluid Drainage | Clear, yellow, or bloody fluid may leak from the affected ear. |
| Hearing Loss | Temporary hearing impairment due to fluid buildup. |
| Irritability | Increased fussiness, particularly in young children. |
| Difficulty Sleeping | Restlessness at night, often worsened by lying flat. |
| Fever | Low-grade or moderate fever may develop. |
Timely Action and Treatment
If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider. They may recommend amoxicillin, especially for bacterial infections. Monitoring and managing symptoms can significantly improve recovery and comfort.
Recommended Amoxicillin Dosage for Children
The typical dosage of amoxicillin for children with otitis media is 80 to 90 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into two doses. For children weighing less than 40 kg, the total daily dose should not exceed 1,000 mg. For those weighing more than 40 kg, the dosage may be guided by adult recommendations, generally 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours.
For moderate to severe infections, the higher end of this dosage range is preferred. Treatment usually lasts for 10 days, ensuring adequate coverage against common pathogens causing otitis media. In cases of recurrent infections, consider adjusting the dosage or the duration based on the child’s history and response to previous treatments.
Be vigilant about monitoring for any signs of allergy or side effects. In case of adverse reactions, consult a healthcare professional for guidance. Always follow the prescribing physician’s instructions regarding dosages and duration to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Recommended Amoxicillin Dosage for Adults
The standard dosage of Amoxicillin for adults with otitis media is typically 500 mg every 8 hours or 875 mg every 12 hours. For more severe infections, the dosage may increase to 1,000 mg every 12 hours. The total duration of treatment generally spans from 5 to 10 days, depending on the specific case and physician recommendation.
For adults with penicillin allergies, alternative antibiotics may be recommended. Always consult a healthcare provider to confirm the appropriate treatment and ensure the correct medication is prescribed.
Hydration and maintaining rest are also significant factors in promoting recovery. Keeping track of symptoms and any side effects from Amoxicillin is advisable, as it aids in timely adjustments to treatment if necessary.
Factors Influencing Amoxicillin Dosage Adjustments
Dosage modifications for Amoxicillin in cases of otitis media rely on various factors. Understanding these variables ensures optimal treatment outcomes.
- Age: Pediatric patients typically require different dosing compared to adults. Children may have a higher metabolic rate, necessitating adjustments based on weight.
- Weight: Body weight plays a critical role in determining the correct dose, particularly in children. The standard recommendation is often based on milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg).
- Severity of infection: More severe otitis media cases may demand higher doses or extended therapy duration to ensure effective management.
- Allergy history: Patients with penicillin allergies may require alternative antibiotics or adjusted doses following a desensitization protocol.
- Renal function: Impaired kidney function can affect drug clearance. Dosing adjustments are necessary to avoid toxicity in patients with reduced renal capacity.
- Presence of comorbidities: Patients with other chronic conditions may require careful monitoring and dose adjustments to manage interactions and side effects.
Continuous monitoring and follow-up are crucial to ensure the appropriate response to treatment. Adjustments to the dosage should be made judiciously based on the patient’s evolving condition.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations with Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin may cause various side effects, and awareness of these can help manage any unexpected reactions. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Monitor your child’s hydration status, as diarrhea can lead to dehydration.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions ranging from rashes to anaphylaxis. If any rash, itching, or swelling occurs, seek medical attention immediately. Document any history of allergies to penicillin or other related antibiotics, as this can guide treatment decisions.
Drug Interactions
Be aware of potential interactions between amoxicillin and other medications. Drugs like probenecid may increase amoxicillin levels in the bloodstream, enhancing effectiveness but also the risk of side effects. Discuss all medications, including over-the-counter products and supplements, with your healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Always complete the full course of amoxicillin prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Stopping prematurely may lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. If side effects become severe or troublesome, contact your healthcare provider for advice on potential alternatives or supportive care.